|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Navigation: Technical Guide > Monitoring and Collecting >
|
File Path and Matches
File Monitor monitors a log file, ASCII file, or text file (or a directory of ASCII or text files). File Monitors parse non-circular text files for words or strings, and notify when the search criteria is found.
Note
Only Service Agents can run a File Monitor, and only local file paths are supported. Virtual Agents, UNC paths and mapped drives are unsupported.
If a new copy of a monitored file is created, the File Monitor will detect this and read it as a new file even though the file name has not changed. Windows file system tunneling can mask this change. See Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 172190 for more details.
When it gets to the end of the file, the File Monitor sets a bookmark. At the next Scheduled Interval it will begin reading new lines in the file after the bookmark. Since the File Monitor reads in a line-by-line fashion, a line that has additional text added to it after being bookmarked will have these characters skipped, and monitoring will begin on the line after the bookmark.
By default, when the File Monitor is first created, it skips to the end of each file it monitors and sets a bookmark. It then starts watching for character string matches in new lines added to the file(s). To force File Monitor to search each file for matches from the beginning, add a checkmark next to Do Actions on First Run.
Paths
Each File Monitor supports one or more search paths. A search path can be a single file or, by using wildcards, a group of files. For example, to search all Internet Information Server logs, use a search path of C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\LOGFILES\*.LOG, and check the Search Subfolders checkbox. This will cause all log files (HTTP, SMTP, NNTP, and FTP) in all of the sub-directories to be searched for the strings specified.
Important
The File Monitor path must include a filename, or a wildcard pattern. For example:
C:\Windows\windowsupdate.log
C:\Windows\kb*.log
A path without a file name or pattern will cause the File Monitor to not do anything.
Add File Path
Each File Monitor supports one or more search paths. To add another file path, click the Add button.
Matches
Enter one or more character strings for the File Monitor search. Use the Add button to add a match, and use the Delete button to remove the selected match. Double-click any listed match string to edit it.
Note
There is an implied OR-operator between each line of the character strings. For example, given the following list of matches:
*error*
*root*
*paycheck*
A line added to a monitored file and containing the string root will be found by the File Monitor.
Add Match
Enter the word or string you want to search for. You can click the Insert Variable button to insert a variable in the search string.
You can use the asterisk (*) as a wildcard character, a pipe (|) as an OR operator, and an ampersand (&) as an AND operator. For example, to search a flat file for the word error OR the word failed, use the following syntax: *error*|*failed*. Be sure to surround the character string with asterisks.
Note
It is not possible to search for strings across multiple lines because the File Monitor reads in a line-by-line fashion. For example, searching for *failed logon* will work if the text is all on one line but if the failed text is on one line, then there is a carriage return in the file with the text logon in the next line, then the File Monitor won't detect it.
Each string match added to the Matches tab will add a corresponding sub-tab to the Actions tab. So File Monitor Actions can be customized for each string found.
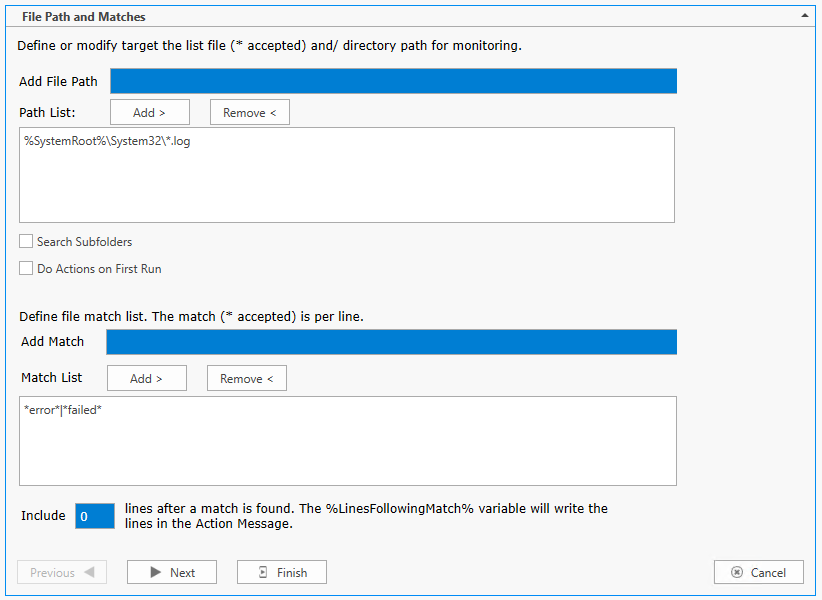
Actions
Custom Action (Warning) 5532 - A custom action is added to the Actions list for each search string entered in the Match list (see Add Match above).
Monitor Assignments
Assign the writer to a group of servers by selecting a monitoring category.
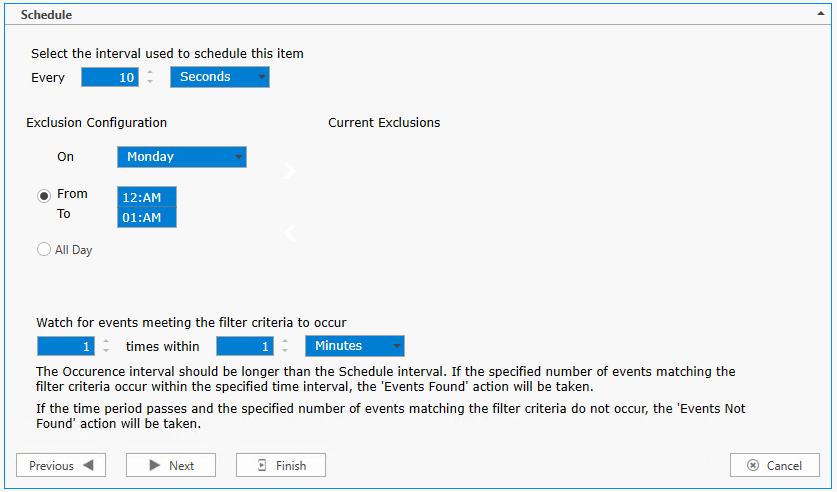
Scheduling
Specify the interval at which the monitoring, polling or action is to occur. Depending on the Monitor Item type, Items can be scheduled in interval increments of Seconds, Minutes, Hours and Days. The Scheduled Interval is relative to the top of the hour or top of the minute. For example, if a Scheduled Interval is configured for 10 minutes, the Monitor Item will execute at hh:10:00, hh:20:00, hh:30:00, hh:40:00, hh:50:00, h1:00:00, etc. If a Scheduled Interval is configured for 15 seconds, the Monitor Item will execute at hh:00:15, hh:00:30, hh:00:45, hh:01:00, hh:01:15, etc.
Exclusion Configuration
Specify day(s) of week when you do not what the scheduled item to run.
Naming
Enter the name of the item and give it a description.
Event Category
This allows you to assign a custom category for the Action event. This custom category may then be used in filtering and notifying later.
Enabled
Use this check box to enable/disable a monitor item.